Scope of Managerial Economics: Key Concepts for Success
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
The Scope of Managerial Economics plays a pivotal role in the effective decision-making process within businesses. It blends economic theory with managerial practice, enabling business leaders to make informed decisions that drive growth and success.
By understanding and applying managerial economics, businesses can optimize their operations, enhance profitability, and achieve strategic objectives.
What is Managerial Economics?
Managerial economics refers to the application of economic concepts and methodologies to solve business problems and guide managerial decision-making.
It involves analyzing various factors like demand, production, cost, pricing, and competition to help businesses make informed choices that align with their long-term objectives.
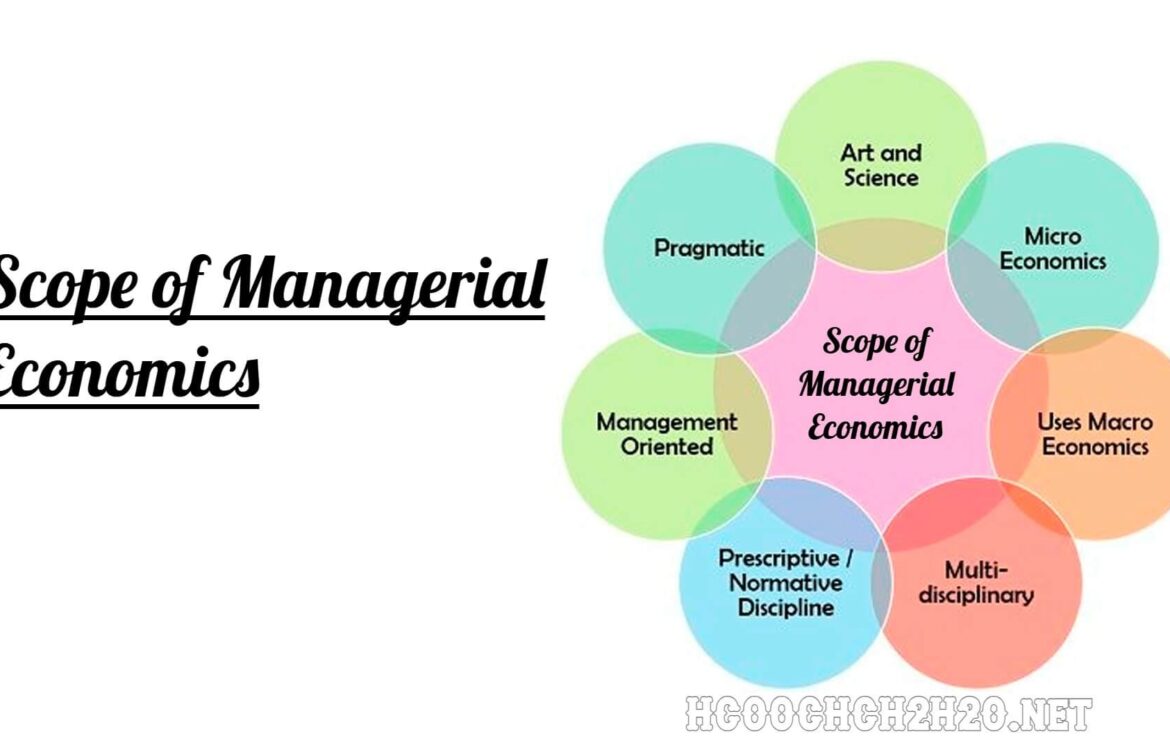
The Scope of Managerial Economics encompasses a wide range of topics, all focused on how economic theories can be applied to business practices.
It provides valuable insights into how firms can efficiently allocate resources, optimize production, and achieve maximum profitability in a competitive market.
Key Areas of the Scope of Managerial Economics
The Scope of Managerial Economics can be broken down into several key areas that are essential for managers to understand. These areas include:
- Demand Analysis and Forecasting
Understanding demand is crucial for businesses to align their production with market needs. Through demand analysis and forecasting, businesses can predict future trends and make strategic decisions related to pricing, production, and inventory management. - Production and Cost Analysis
The relationship between input and output is fundamental to every business. Managers must understand how to optimize production processes to reduce costs and maximize output. The Scope of Managerial Economics includes evaluating cost structures, economies of scale, and production efficiency. - Pricing Decisions and Strategies
Setting the right price for a product or service is one of the most important managerial decisions. The Scope of Managerial Economics includes analyzing market conditions, competitive pricing, and customer demand to develop effective pricing strategies that maximize revenue. - Market Structure and Competition
Businesses operate in different market structures such as perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. Understanding these market dynamics allows managers to make better strategic decisions in response to competition. - Risk and Uncertainty Analysis
All businesses face uncertainty, whether due to market fluctuations, economic conditions, or internal challenges. Managerial economics helps businesses assess risk, use forecasting models, and make decisions that mitigate potential losses. - Capital Budgeting
Capital budgeting involves making decisions on long-term investments, such as purchasing new equipment or expanding operations. The Scope of Managerial Economics covers techniques for evaluating investment opportunities, including cost-benefit analysis, payback period, and net present value (NPV). - Pricing and Output Decisions
The Scope of Managerial Economics also covers how businesses determine the optimal level of output and pricing to maximize profits, considering factors like market demand, competition, and production capacity.
The Role of Managerial Economics in Decision-Making
The Scope of Managerial Economics is deeply connected to decision-making at every level of an organization. From high-level strategic decisions to day-to-day operations, managerial economics provides a framework for making informed choices that balance profitability with efficiency.
For instance, when determining the optimal price for a product, a business must consider not only the cost of production but also market demand and competitive pricing.
Managerial economics uses tools like elasticity of demand and marginal analysis to determine the most advantageous price point.
Optimizing Resource Allocation
One of the primary goals of managerial economics is to ensure the efficient use of resources. By analyzing production costs, resource availability, and market conditions, businesses can allocate their resources more effectively.
This can result in lower operational costs, better-quality products, and improved customer satisfaction.
Strategic Planning and Forecasting
The Scope of Managerial Economics is also vital in strategic planning and forecasting. Managers use economic models and data analysis to predict future trends, market conditions, and consumer behavior.
This allows companies to plan for long-term success, making decisions that align with both current and future business environments.
How the Scope of Managerial Economics Impacts Business Growth
The application of Managerial Economics has a direct impact on business growth. By understanding economic principles, managers can make decisions that drive profitability and expand market share.
Profit Maximization
One of the key objectives of managerial economics is profit maximization. This can be achieved by optimizing pricing, reducing costs, improving efficiency, and increasing customer satisfaction.
Managers use economic principles to ensure that every decision contributes to the bottom line.
Market Expansion and Diversification
The Scope of Managerial Economics also plays a significant role in market expansion and diversification strategies.
By analyzing market trends, competition, and consumer behavior, businesses can identify opportunities for growth, such as entering new markets or diversifying their product lines.
The Role of Managerial Economics in Financial Management
Managerial economics provides essential tools for financial management, helping businesses make informed decisions regarding investments, financing, and budgeting.
By understanding concepts like interest rates, inflation, and market behavior, managers can make better financial decisions that lead to higher returns on investments and cost savings.
Investment Decisions
Managerial economics is crucial for making investment decisions that align with the company’s goals.
Through techniques like net present value (NPV) and internal rate of return (IRR), managers can evaluate potential investments, assess risks, and determine the best course of action for maximizing returns.
Cost Control and Budgeting
In the context of financial management, Managerial Economics helps businesses control costs and set realistic budgets.
Managers can analyze cost structures, identify inefficiencies, and implement cost-cutting measures that improve the company’s financial health.
The Relationship Between Managerial Economics and Business Strategy
The Scope of Managerial Economics is closely tied to business strategy. By applying economic principles, businesses can develop strategies that maximize their competitive advantage.
This includes evaluating market conditions, assessing competitors, and determining the best approach to marketing and sales.
For instance, if a company operates in an oligopoly, where there are few competitors, managerial economics can help the company determine pricing strategies and how much to produce.
Understanding the competition and market dynamics is critical for formulating a successful business strategy.
The Growing Importance of Managerial Economics in the Modern Business Environment
In the ever-changing global economy, the importance of Managerial Economics has grown. Today’s businesses face complex challenges such as globalization, technological advancements, and rapidly shifting consumer preferences.
Managerial economics provides the tools needed to navigate these challenges and adapt to a constantly changing environment.
Adapting to Technological Changes
With technology evolving at a rapid pace, managerial economics helps businesses adapt to changes and make decisions about adopting new technologies.
Whether it’s investing in automation, data analytics, or digital marketing, understanding the economic implications of these decisions is crucial for business success.
Navigating Global Markets
In an increasingly globalized economy, businesses must understand international markets and the impact of global economic conditions on their operations.
Managerial economics provides insights into trade policies, exchange rates, and international competition, helping businesses make informed decisions in global markets.
Managerial Economics in Different Industries
The Scope of Managerial Economics extends across various industries, including manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and technology.
Each industry faces unique challenges and opportunities, but the core principles of managerial economics apply universally.
Manufacturing and Cost Management
In the manufacturing sector, managerial economics plays a key role in cost management and production optimization.
By analyzing production costs, supply chain efficiency, and market demand, managers can make informed decisions that improve profitability and reduce waste.
Healthcare and Resource Allocation
In healthcare, managerial economics is essential for resource allocation, pricing strategies, and cost control. Healthcare managers use economic models to allocate limited resources effectively and ensure that services are delivered efficiently without compromising quality.
Retail and Pricing Strategies
For retailers, the Scope of Managerial Economics involves pricing strategies, inventory management, and consumer behavior analysis.
Managers must balance the need to attract customers with the need to maintain profitability, making pricing decisions a key focus of managerial economics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Scope of Managerial Economics is vast and plays a crucial role in the success of businesses. By applying economic principles to everyday decision-making, managers can optimize resource allocation, drive profitability, and plan for long-term growth.
From pricing strategies to investment decisions, managerial economics provides the insights needed to make informed choices that lead to sustainable success.
Understanding the core concepts of managerial economics equips business leaders with the tools they need to navigate an ever-changing business landscape, adapt to market shifts, and achieve their objectives.
By integrating managerial economics into business practices, companies can ensure they are well-positioned for future growth and success.
You may also like
You may be interested
SFDC: Transforming Customer Relationships with Cloud Tech
Introduction SFDC, short for Salesforce.com, has revolutionized the way businesses...
Sad Shayari: Heartfelt Poetry to Express Your Deep Emotions
Introduction Sad Shayari is an emotional form of poetry that...
Top 10 Napkins for Parties, Weddings, and Events
Introduction Napkins are a small but essential detail for any...
Leave a Reply